Understanding the presence and abundance of parasitoid species of Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) (Diptera: Drosophilidae) is crucial for the establishment and execution of a biological control strategy targeting Drosophila, an invasive pest that infests maturing delicate-skinned berries and stone fruits in both natural and cultivated environments.
The purpose of the study was to develop the available knowledge on parasitoid community of Drosophilidae in the tart cherry agroecosystem. Additionally, it aimed to identify landscape factors that have a role in the successful implementation of future augmentative and classical biological control releases.
To achieve this objective, a comprehensive field survey was undertaken to ascertain the composition of the parasitoid community that is closely linked with locations infested by D. suzukii in tart cherry orchards and woodlots located in the western, northwestern, and central regions of Michigan (USA).
Sentinel traps, containing larvae and pupae of Drosophila suzukii, were strategically positioned throughout the central areas of tart cherry orchards, as well as in woodlots that bordered these orchards, and in woodlots that were geographically apart from any known commercial host of D. suzukii. The placement of traps started in July 2021 and continued until October 2021.
Three parasitoid species, which have been documented to utilise drosophilids as hosts, were retrieved from the aforementioned traps. Pachycrepoideus vindemiae (Rondani) (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) and Leptopilina boulardi (Barbotin, Carton & Keiner-Pillault) (Hymenoptera: Figitidae) were observed to have emerged from the banana fruit that were infested by Drosophila.
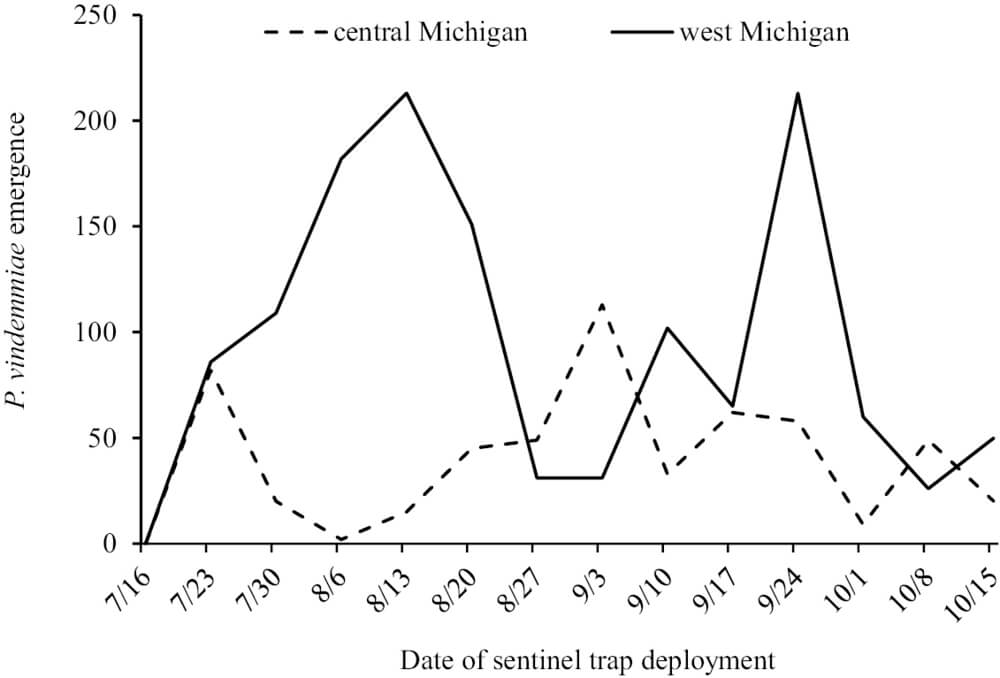 Figura 1: Emersione totale di P. vindemiae dalle trappole sentinella settimanali per pupe di D. suzukii nel Michigan occidentale (n = 6) e centrale (n = 11).
Figura 1: Emersione totale di P. vindemiae dalle trappole sentinella settimanali per pupe di D. suzukii nel Michigan occidentale (n = 6) e centrale (n = 11).
The adult form of Leptopilina heterotoma (Thomson) was obtained through collection in a sentinel trap. Within the group of wasps studied, it was observed that only P. vindemiae exhibited successful parasitism of D. suzukii pupae under laboratory conditions. The pupal parasitoid exhibited a high population density and broad geographical distribution in both cherry orchards and woodlots.
The orchards yielded the maximum number of P. vindemiae specimens, followed by woodlots in close proximity to orchards, whereas woodlots without surrounding planted fruit had the lowest frequency of detections. The higher prevalence in woodlots that were in close proximity to cultivated cherry orchards can be attributed to the fact that D. suzukii and other Drosophila populations tend to be more abundant in places where there is greater availability of fruit.
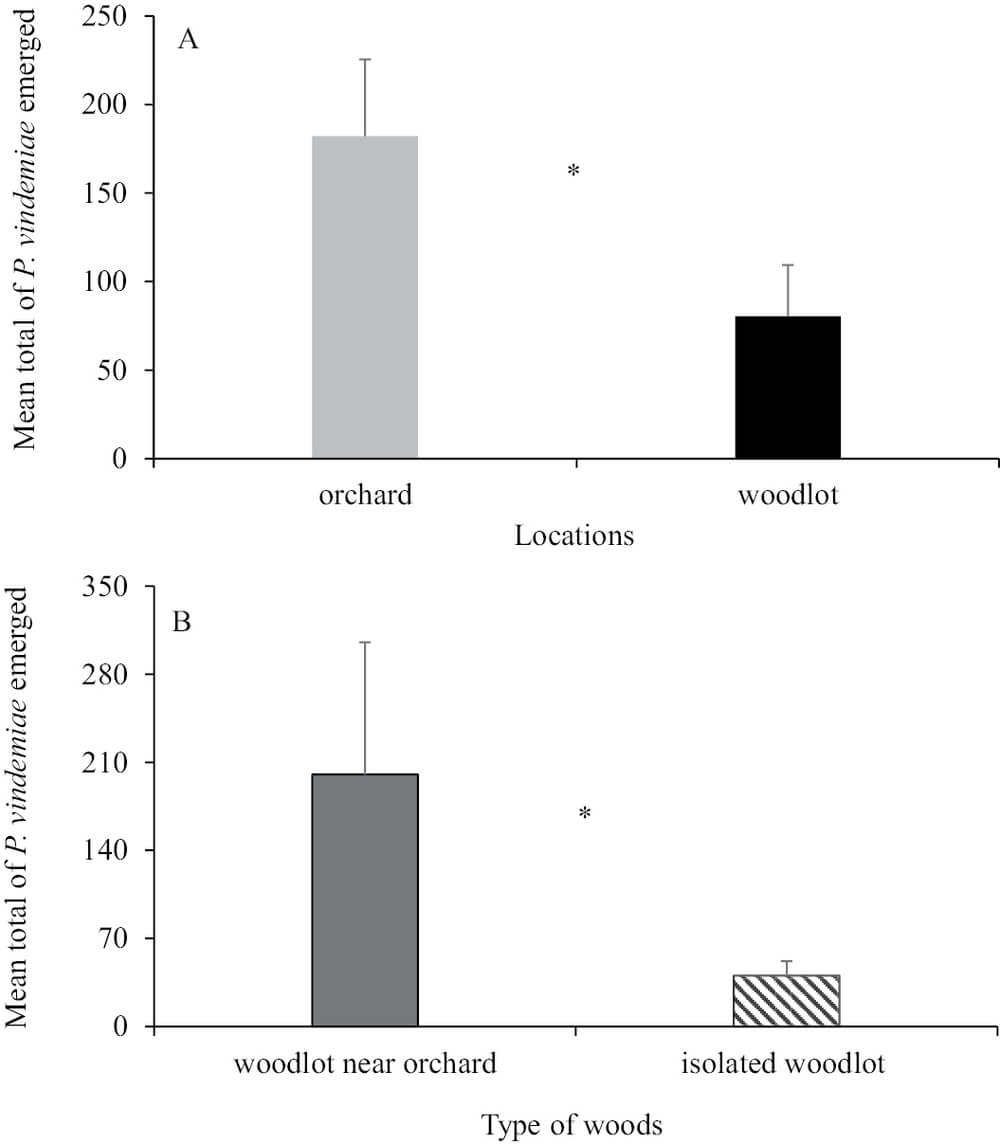 Figura 2: Numero totale medio di P. vindemiae (+SEM) emerse durante un periodo di campionamento di 14 settimane tra le trappole sentinella collocate nei frutteti e quelle collocate nei boschi senza frutteti nelle vicinanze (A) e tra le trappole sentinella collocate nei boschi adiacenti ai frutteti e in quelli senza frutteti nelle vicinanze (B).
Figura 2: Numero totale medio di P. vindemiae (+SEM) emerse durante un periodo di campionamento di 14 settimane tra le trappole sentinella collocate nei frutteti e quelle collocate nei boschi senza frutteti nelle vicinanze (A) e tra le trappole sentinella collocate nei boschi adiacenti ai frutteti e in quelli senza frutteti nelle vicinanze (B).
The results of this study indicate that the use of augmentative or traditional biological control agents for D. suzukii in orchards after harvest may prove to be effective in managing late-season populations of this pest. Significantly, P. vindemiae exhibited the highest abundance within cherry orchards subsequent to the harvest period, indicating their ability to navigate this agroecosystem despite the likely presence of residual chemical applications that are regularly utilised in such systems.
Nevertheless, it is worth noting that their presence during the growth season, when regular insecticide applications are administered, could potentially be reduced dramatically due to chemical exposure.
Further investigation is required to clarify the impact of pesticide usage, both during the growing season and after harvesting, on the efficacy of existing and prospective biological control methods, as well as deepening the biological cycles of other potential parasitoids of Drosophila suzukii.
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












