Sour cherries are non-climacteric fruits that are susceptible to rapid quality degradation after harvest. Developing and applying efficient storage and packaging strategies to mitigate post-harvest degradation, however, can help to improve storage. Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) it is a strategy that can be effectively combined with cold storage.
MAP is used to delay senescence, reduce post-harvest pathophysiology and slow degradation in many vegetable products for fresh consumption. Little is currently known on the use of MAP in sour cherries, although it has already been shown to have a positive effect on both weight loss and slowing fruit deterioration.
The study carried out in collaboration between research institutions from Italy, Hungary and the Czech Republic had a twofold objective. The first: to evaluate the shelf-life of sour cherries that were freshly picked and cold stored under standard and MAP atmospheric conditions in three cultivars: ‘Érdi bőtermő’, ‘Újfehértói fürtös’ and ‘Petri’.
The second, to evaluate the incidence of degradation of harvested and cold stored fruits in combination with MAP as a function of cultural management (conventional, integrated pest management [IPM] and reduced IPM) for the cv. ‘Érdi bőtermő’.
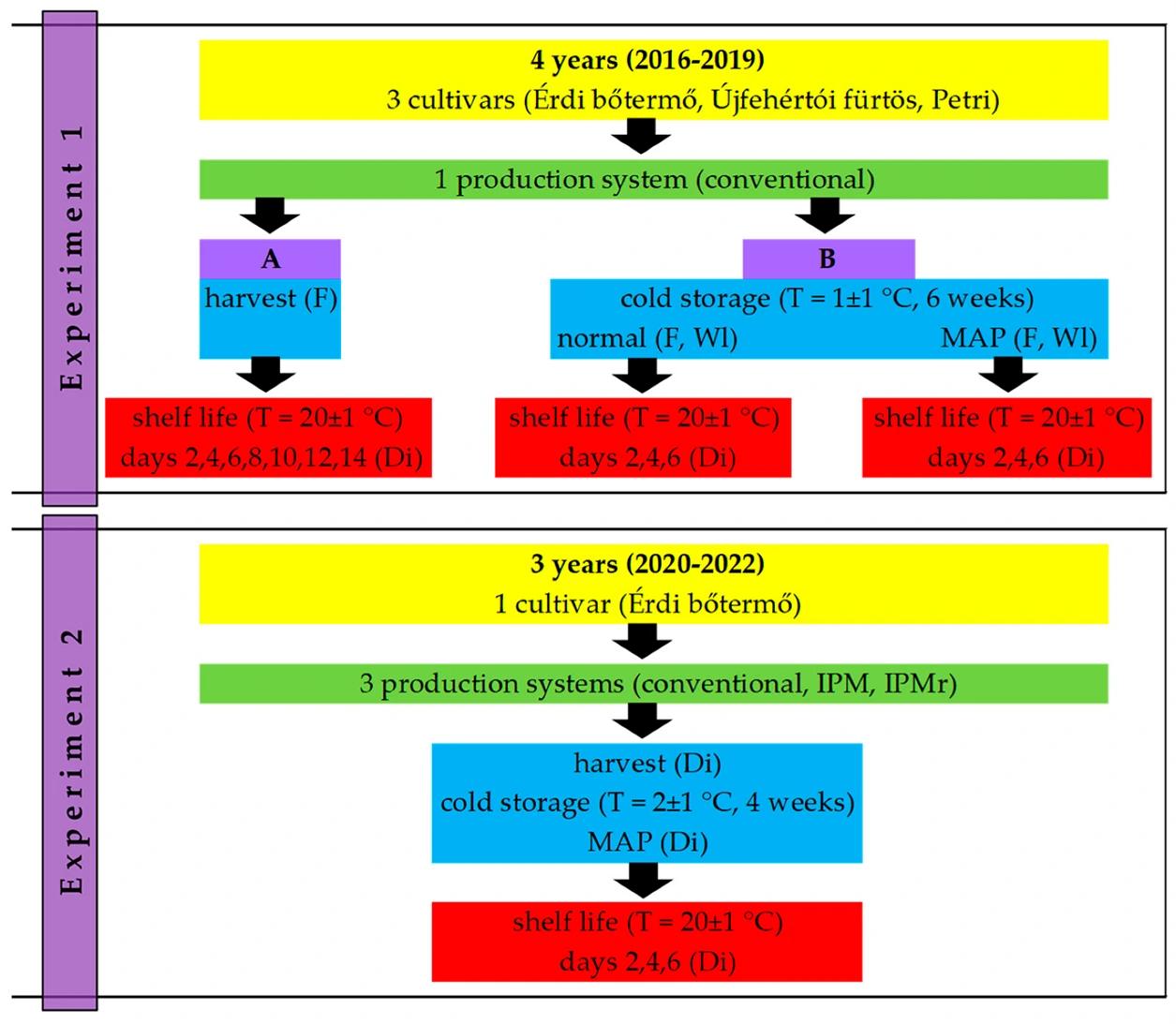 Image 2: Experimental design for experiments 1 and 2. Experiment 1A: three sour cherry cultivars were harvested and stored at 20 ± 1 °C (shelf-life) for 14 days. Experiment 1B: three sour cherry cultivars were harvested and stored at 1 ± 1 °C (cold storage) with normal atmosphere (NA) or modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) for 6 weeks. After this, fruits were further stored at 20 ± 1 °C (shelf-life) for 6 days. Experiment 2: one sour cherry cultivar in 3 production systems (conventional; integrated pest management, IPM; and reduced integrated pest management, IPMr) was harvested and stored at 2 ± 1 °C (cold storage) with modified atmosphere packaging for 4 weeks. After this, fruits were further stored at 20 ± 1 °C (shelf-life) for 6 days. Overall decay incidence (Di), fruit firmness (F), and fruit weight loss (Wl) were determined where they were indicated in brackets. Source: Sandor et al, 2024.
Image 2: Experimental design for experiments 1 and 2. Experiment 1A: three sour cherry cultivars were harvested and stored at 20 ± 1 °C (shelf-life) for 14 days. Experiment 1B: three sour cherry cultivars were harvested and stored at 1 ± 1 °C (cold storage) with normal atmosphere (NA) or modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) for 6 weeks. After this, fruits were further stored at 20 ± 1 °C (shelf-life) for 6 days. Experiment 2: one sour cherry cultivar in 3 production systems (conventional; integrated pest management, IPM; and reduced integrated pest management, IPMr) was harvested and stored at 2 ± 1 °C (cold storage) with modified atmosphere packaging for 4 weeks. After this, fruits were further stored at 20 ± 1 °C (shelf-life) for 6 days. Overall decay incidence (Di), fruit firmness (F), and fruit weight loss (Wl) were determined where they were indicated in brackets. Source: Sandor et al, 2024.
In addition, the flesh firmness and weight loss of the fruit was evaluated for all three cultivars in order to conduct an in-depth analysis of their overall quality characteristics prior to the evaluation of shelf life. Modified atmosphere packaging (Xtend® Cherry, StePac LA Ltd.) effectively preserved or slightly increased flesh firmness compared to the control fruits.
Compared to conventional storage, modified atmosphere packaging also resulted in a substantial reduction in fruit weight loss. The incidence of decay was similar among all cultivars considered but still presented low values after six weeks of cold storage in normal atmosphere. The quality of the sour cherries was maintained during cold storage with both normal and modified atmosphere packaging.
However, the shelf life of the fruit was substantially reduced once the fruit was brought to shelf-life temperature, regardless of storage methods.
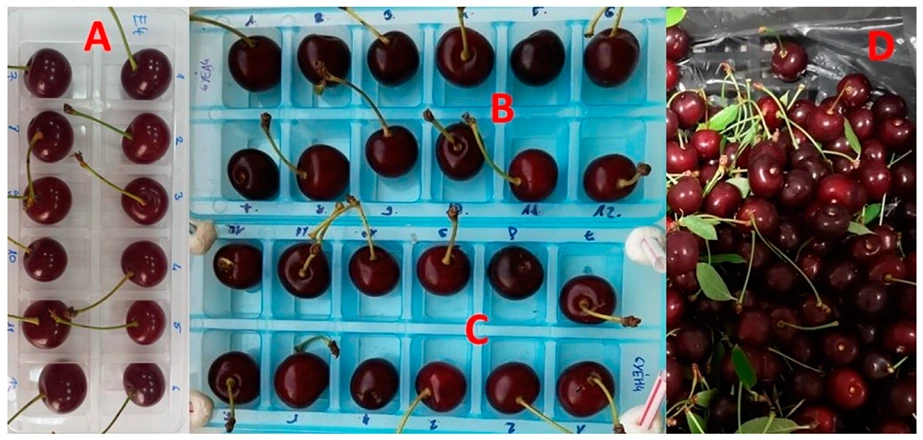 Image 2: Twelve fruits (one repetition) in each of the three trays for shelf-life conditions (A–C) and fruits in modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) bag after 6-week cold storage (D) for sour cherry cv. ‘Érdi bőtermő’. Source: Sandor et al, 2024.
Image 2: Twelve fruits (one repetition) in each of the three trays for shelf-life conditions (A–C) and fruits in modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) bag after 6-week cold storage (D) for sour cherry cv. ‘Érdi bőtermő’. Source: Sandor et al, 2024.
However, the post-harvest storage capacity of sour cherry fruits can be significantly influenced by cultivar genetics, environmental conditions and cultural practices. Conventional or IPM systems showed the lowest incidence of fruit rot after the combination of modified atmosphere packing and cold storage conditions for 4 weeks.
The reduced IPM system showed the highest incidence of fruit rot at harvest, which was substantially higher than that observed in the conventional and IPM systems. The incidence of fruit rot was observed in the order: conventional < IPM < reduced IPM, during cold storage in combination with MAP.
The only significant differences were observed between conventional and reduced IPM systems. These results indicate that sour cherries produced using conventional or IPM systems and subsequently cold stored for four weeks under modified atmosphere packaging conditions are optimally preserved. This means that the research has contributed to the development of a sour cherry storage protocol that is also suitable for commercial applications.
Source: Sándor, E.; Mihály, K.; Nagy, A.; Pál, K.; Peles, F.; Zabiák, A.; Kovács, C.; Takács, F.; Romanazzi, G.; Holb, I.J. Effects of Storage Conditions, Cultivars, and Production Systems on Fruit Decay Incidence of Sour Cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) Fruit after Shelf-Life Conditions. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102212.
Images: SL Fruit Service; Sandor et al, 2024.
Melissa Venturi
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved