Climate change is transforming the seasonal cycles of plants, including key processes such as flowering. A study conducted on Hachijojima Island in Japan analyzed the behavior of the Yoshino cherry tree (Cerasus x yedoensis) at the southern limits of its distribution, collecting data from 1948 to 2024.
The aim was to understand the relationships between two crucial parameters for flowering: cold exposure, necessary for dormancy release (chilling requirement), and heat required for bud development (heat requirement). This study provides a detailed picture of the effects of global warming on the phenological cycles of this species, showing how even modest variations in seasonal temperatures can significantly delay or even prevent flowering.
The study focused on Hachijojima due to its distinctive climate, characterized by relatively mild winters and temperate springs. The first flowering date was correlated with daily average temperatures, distinguishing between cold exposure periods (<10 °C) and heat accumulation periods (≥10 °C). The results revealed that in years with warmer winters, cold exposure was insufficient, leading to significant delays in flowering, sometimes by weeks compared to the climatic norm.
A particularly noteworthy winter was 2023–2024, marked by temperatures 1.0–1.6 °C above the seasonal average. Under these conditions, the first flowering date occurred on April 15, much later than in years with colder winters. The relationship between cold exposure and heat requirement was modeled mathematically using linear and logarithmic functions, which showed a significant correlation: the greater the cold exposure, the lower the heat requirement, and the earlier the flowering.
The study highlighted two main patterns influencing the flowering date. In the first, colder winters accelerate the transition from dormancy to bud growth; if spring temperatures are warm, flowering occurs rapidly, while colder spring temperatures slow down development. In the second pattern, milder winters delay dormancy release, requiring higher spring temperatures to compensate for the delay. However, if spring temperatures remain low, the delay in flowering becomes even more pronounced.
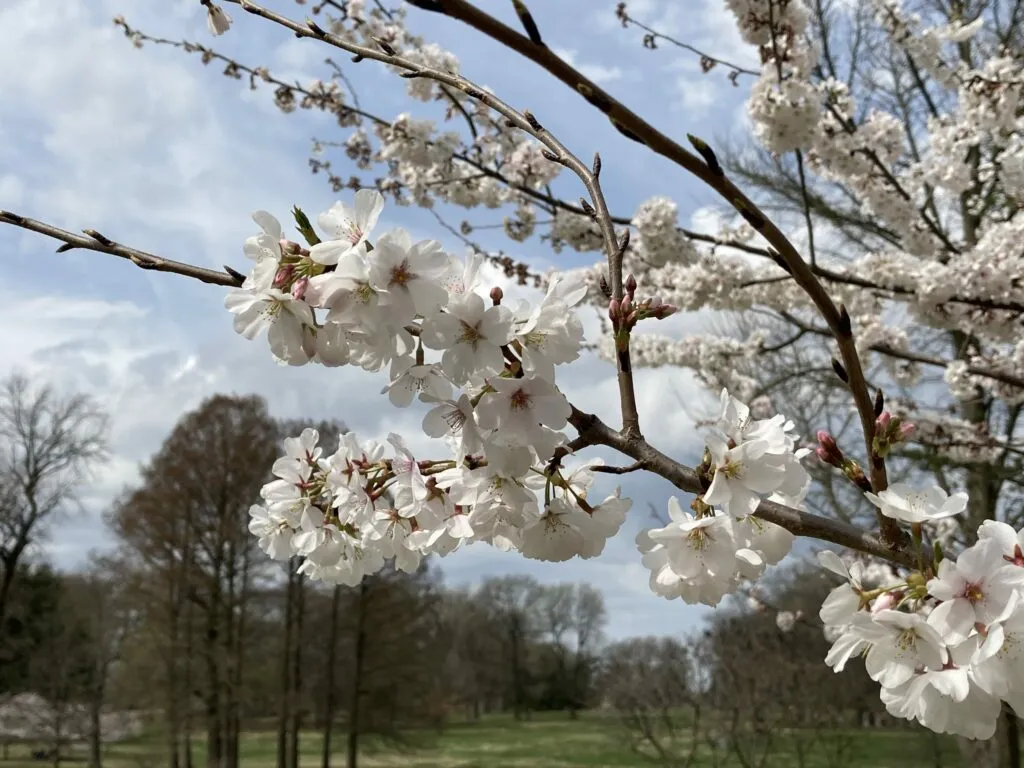

Climate change poses a growing challenge for the Yoshino cherry tree, particularly in regions at the southern edge of its distribution. The lack of sufficiently cold days during winter could prevent flowering in the future, jeopardizing the survival of the species in these areas. This is
particularly evident considering that despite the increase in spring temperatures observed since 1948, the average flowering date has not shown significant trends, suggesting that the system is already at the limit of climatic compensation.
The findings of this research not only offer a detailed understanding of the phenomenon but also have practical implications. Understanding the dynamics of cold exposure and heat requirement can help develop more accurate predictive models for flowering, essential for managing and protecting this iconic species. Furthermore, preserving the Yoshino cherry, a symbol of Japanese spring, will require targeted adaptation strategies, such as selecting more resilient varieties or identifying favorable microclimates.
It remains essential to monitor climate change and its impact on plants. Studies like this are crucial to anticipate the ecological and social consequences of global warming and to develop solutions that can mitigate its most dramatic effects.
Source: Shin, N., Saitoh, T. M., Takasu, H., & Morimoto, H. (2024). Influence of climate change on flowering phenology of Yoshino cherry at its southern distribution limit. International Journal of Biometeorology, 1-5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-024-02797-0.
Images: Planet Naturale; Forest ReLeaf
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (IT)
Cherry Times - All rights reserved