Drosophila suzukii, also known as spotted-wing fruit fly, is currently one of the main insect pests in global fruit growing.
This insect is capable of causing severe damage to production in various species, such as cherry, blueberry, raspberry, and strawberry (fleshy fruits).
It is particularly feared for its ability to lay eggs in ripening fruits, making them unmarketable and causing significant economic losses, which in some cases exceed 80%.
Containment strategies have so far mainly relied on synthetic chemical insecticides (and anti-insect nets), but the increasing occurrence of resistance and the environmental impact of these products make the development of effective and eco-friendly alternatives increasingly urgent.
Nanoparticles for pest control
A recent study, in this context, tested the synthesis and use of chitosan-coated silver nanoparticles (AgChNPs), which have proven to be a new and promising weapon for Integrated Pest Management (IPM).
The researchers developed the production of AgChNPs through a biosynthesis process using the liquid extract from leaves of Galega officinalis.
Physico-chemical analyses confirmed the presence of spherical, crystalline, polydisperse, and stable nanoparticles: surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was characterized via UV-vis spectroscopy, which showed a peak at about 420 nm, while X-ray diffraction (XRD) revealed the structure, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) confirmed their morphology and size (from 2.8 to 65.3 nm).
Biological efficacy on Drosophila suzukii
The biological tests conducted on Drosophila suzukii showed high effectiveness at both larval and pupal levels: at the highest concentration (1000 ppm), cumulative mortality (larvae + pupae) reached 73.3% (while at 500 ppm it was 48.3%).
In addition, adult emergence was significantly impaired, dropping from 76.7% in the negative control to 26.7% in the AgChNP-treated group at the highest concentration, clearly reducing the insect’s reproductive and colonization capacity.
Even more significant was the high rate of malformations and morphological alterations observed in surviving adult insects: about 62.8% emerged with wing malformations and about 37.2% showed cuticle demelanization.
These alterations add to direct mortality and suggest a strong sublethal impact of the nanomaterials on the insect’s physiology and reproductive capacity.
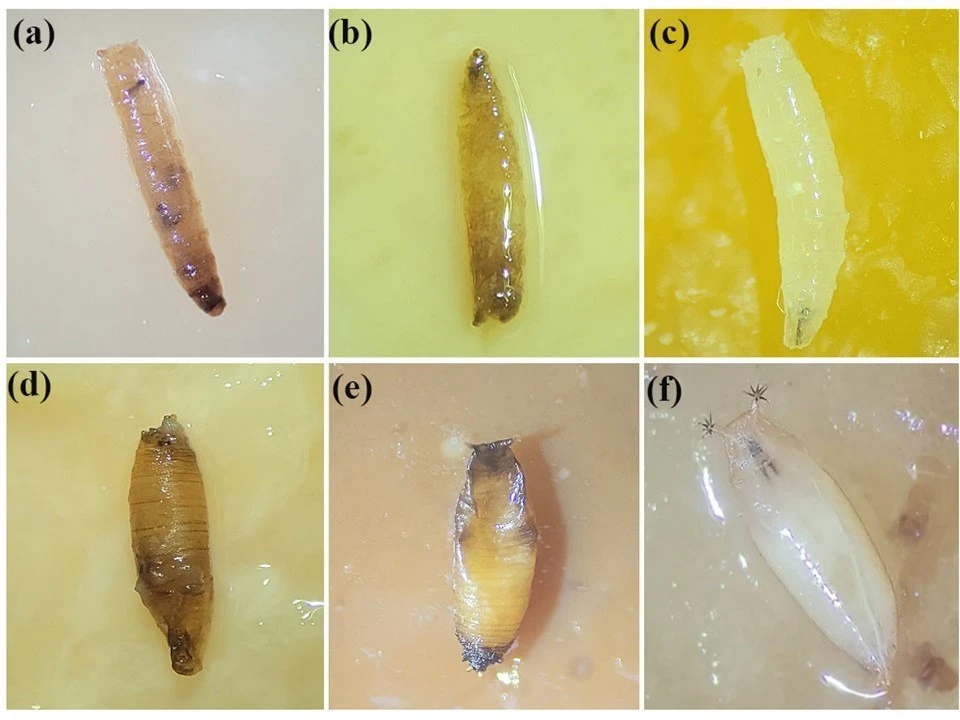 Figure 1. Drosophila suzukii individuals subjected to treatment with biosynthesized AgChNPs at 1000 ppm. (a,b) 2nd-instar larvae after treatment with biosynthesized AgChNPs. (c) Untreated healthy larvae. (d,e) Pupae after treatment with biosynthesized AgChNPs. (f) Untreated healthy pupae.
Figure 1. Drosophila suzukii individuals subjected to treatment with biosynthesized AgChNPs at 1000 ppm. (a,b) 2nd-instar larvae after treatment with biosynthesized AgChNPs. (c) Untreated healthy larvae. (d,e) Pupae after treatment with biosynthesized AgChNPs. (f) Untreated healthy pupae.
Toward sustainable pest management
At the adult stage, AgChNPs also showed rapid and high mortality, with rates between 81.3% and 96% after 48 hours of exposure, results comparable to those of traditional chemical treatments.
This study confirms the high potential of chitosan-coated nanoparticle-based products as an innovative and safe tool for controlling Drosophila suzukii and other phytophagous insects.
The biosynthesis of AgChNPs combines efficacy with greater sustainability, providing a valid alternative for integrated pest management and helping to reduce dependence on traditional pesticides.
Further studies to explore the mechanisms of action and physiological processes could refine and make the application of these products in crop protection even more targeted and safe.
Source: Martínez-Cisterna, D., Rubilar, O., Chen, L., Lizama, M., Chacón-Fuentes, M., Quiroz, A., Parra, P., Rebolledo, R., & Bardehle, L. (2025). Biosynthesized Chitosan-Coated Silver Nanoparticles: Insecticide Activity and Sublethal Effects Against Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Biomolecules, 15(4), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040490
Figure source: Martinez-Cisterna et al., 2025
Andrea Giovannini
University of Bologna (ITA)
Italian Berry - All rights reserved











