The Importance of protecting varietal innovations
Cherry tree cultivation has been a fundamental part of European agriculture for centuries. The protection of new plant varieties through Community Plant Variety Rights (CPVR) is vital for advancing agriculture, protecting breeders' economic interests, and enhancing biodiversity.
The CPVR system, administered by the Community Plant Variety Office (CPVO), grants exclusive rights to breeders, encouraging them to invest in developing new varieties, ultimately benefiting consumers with higher-quality produce.
These protected varieties are covered by specific intellectual property rights, ensuring that breeders have exclusive commercial rights to their new plant varieties for a set period. This protection promotes innovation and research within the agricultural sector.
Current trends in cherry tree CPVR applications
Data from the CPVO reveals a strong interest from breeders in developing new cherry varieties. This interest is driven by increasing consumer demand for high-quality cherries, advancements in breeding techniques, and the economic potential of improved varieties. While apple and pear varieties dominate the landscape, cherry varieties also hold a significant portion of the market.
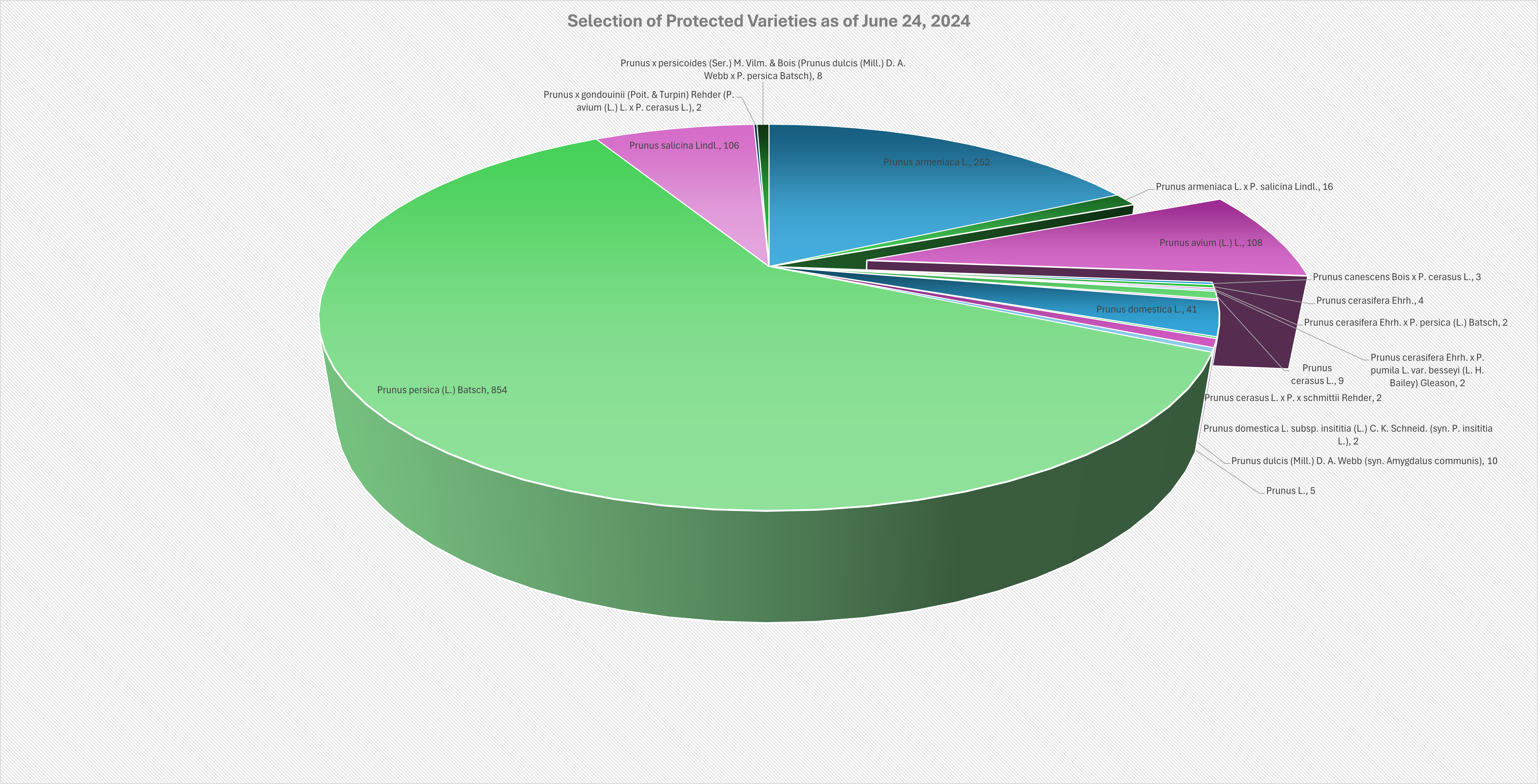 Image 1:
Image 1:
In Italy, Prunus avium (sweet cherry) has seen 24 CPVR applications over the years. Prunus avium ranks third in the number of applications within the Prunus family, following Prunus persica (122 applications) and Prunus armeniaca (38 applications).
Top Countries for Prunus avium applications:
France leads with 46 applications, indicating a robust interest in cherry variety protection. Germany and Italy also show significant engagement. Overall, 108 CPVRs have been granted for Prunus avium, with 90 still active.
Investment in cherry varieties: leading the charge
Investment in cherry CPVR comes from a diverse range of stakeholders, including private breeders, research institutions, and agricultural companies. These groups recognize the commercial potential of developing superior cherry varieties.
Private Breeders and Breeding Companies: These entities are pivotal in cherry breeding, often collaborating with research institutions to commercialize successful varieties. Research Institutions: Institutions like the Julius Kühn-Institut in Germany and the University of Bologna in Italy play a significant role in cherry breeding.
Agricultural Corporations: Large agricultural companies invest heavily in CPVR for cherries to secure exclusive rights to new varieties, gaining a competitive market edge.
Conclusion
The protection of varietal innovations through CPVR is essential for the advancement of agriculture and the economic viability of breeders. The rise in CPVR applications for cherry varieties highlights the growing importance of this fruit in Europe. Private breeders, research institutions, and agricultural corporations are driving this trend.
As the demand for high-quality cherries increases, CPVR's role in protecting innovations becomes increasingly crucial. Encouraging the development of new cherry varieties not only benefits breeders but also enhances produce quality and diversity for consumers. The future of cherry cultivation in Europe looks promising, supported by ongoing investments and a strong CPVR system.
Francesco Mattina
President of CPVO
Cherry Times - All rights reserved











