Cherry production represents an excellence of our territory that has to face important problems, among which, the control of Drosophila suzukii and the prevention of fruit cracking. Monitoring, alternative products, biological control and multifunctional nets are the technological innovations being studied with a view to integrated and sustainable management of these adversities.
The 2023 cherry crop year was negatively affected by spring frost and heavy rainfall in May and June (around 400 mm of rain), resulting in production losses due to fruit splitting, particularly on early and medium-early cultivars.
Analysing, on the other hand, the data from the territorial monitoring of D.suzukii, the current year showed a lower initial population level than in the last three years, but an important demographic increase after the first ten days of June, favoured by the rainy weather, which necessitated an intensification of insecticide interventions and caused difficulties in the control of late varieties.
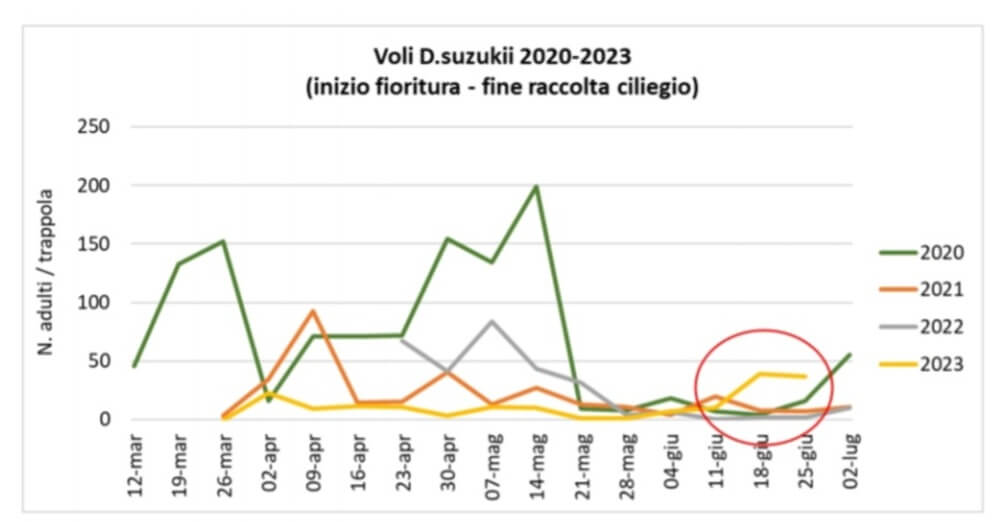 Figure 1: Catch trend of D. suzukii 2020-2023 in the province of Modena - Territorial monitoring Modena Phytosanitary Consortium.
Figure 1: Catch trend of D. suzukii 2020-2023 in the province of Modena - Territorial monitoring Modena Phytosanitary Consortium.
In order to cope with these adversities, an extensive experimental activity is underway which has provided promising indications that nevertheless require a few years of further verification. Below is a summary of the results obtained to date.
Biological control of D.suzukii with the exotic parasitoid Ganaspis brasiliensis
In recent months the third year of activity of the national biological control programme with the exotic parasitoid Ganaspis brasiliensis for the control of D.suzukii was completed. In Emilia-Romagna releases were carried out at 20 sites, 12 of which in the province of Modena with interventions carried out in 3 phases, in the period from June to September. This is a 'classic biological control' programme with 'inoculation' of the environment with small quantities of the parasitoid in order to favour its gradual establishment in space and time.
Although parasitisation rates are currently only a few percent, the results to date are promising, as G. brasiliensis has shown that it is able to reproduce on the host and survive the winter.
Another positive fact is the spontaneous discovery of another exotic parasitoid, Leptopilina japonica, which currently represents the species with the highest parasitisation rate. We confidently await the establishment and spread of these antagonists, which in the near future may be able to create a balance and thus reduce the populations of the Asian midge.
Investigation of new Attact&Kill methods for the control of D.suzukii
The project, in its second year of activity, is the result of a collaboration between the Experimental Centre of Laimburg (BZ), the Plant Protection Consortium of Modena, ASTRA - Innovation and the University of Verona. Investigations are underway to develop the Attract&Kill method, thanks to the availability of attractants obtained from yeasts of the fungus Hanseniaspora uvarum activated with low doses of the biological insecticide Spinosad.
The potential interest for this technique lies in the fact that the applications of the attractant+insecticide mixture do not involve open-field interventions but only limited to a central vegetation strip of one meter. The results of the second year of trials confirm the effectiveness of this method, which showed performance comparable to open-field treatment.
The activities will have to continue in the coming years, but it will then be necessary to assess the interest of the companies in the sector, to acquire the formulation, in order to proceed with the necessary registration and distribution process on the market.
Evaluation of multifunctional covers models for cherry trees
The project currently underway at the experimental fields of the 'ex-Impresa Mancini' in Vignola, has provided for the realisation and comparison of different models of multifunctional covering made with special ultra-flexible rainproof nets closed at the perimeter with anti-drosophila nets.
The results of the first three years of activity show interesting responses in terms of control of D. suzukii, and reduction of insecticide treatments compared to uncovered. There was also a good response in terms of rain protection and reduction of cracking. A summary of the results is given in table 1.
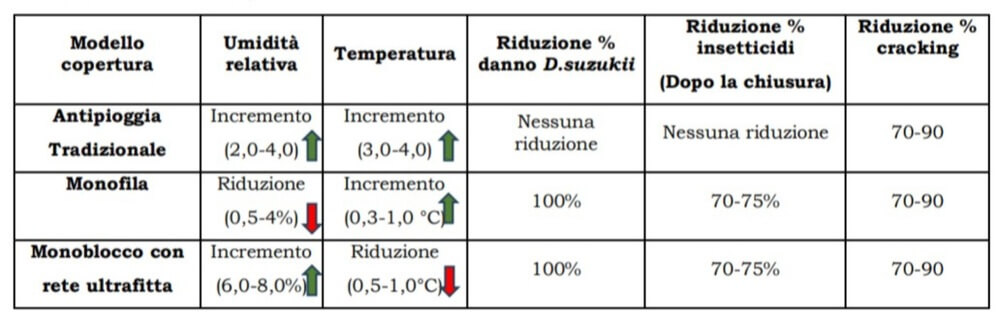 Figure 2: Main characteristics of cover models Vs. an uncovered cherry orchard (average of 2021-2023 observations).
Figure 2: Main characteristics of cover models Vs. an uncovered cherry orchard (average of 2021-2023 observations).
The objectives for the next few years also concern in-depth studies on the influence of the microclimate, alterations in the light spectrum, influences on the physiology of the plant, the possibility of savings in irrigation, qualitative-quantitative aspects of production and the management of the organically protected cherry tree. The activity is carried out in collaboration with the Vignola Cherry Consortium and the University of Bologna.
Source: Modena Phytosanitarium Consortium
Images: Emilia-Romagna Region
Cherry Times - All rights reserved












